Kubernetes 作为一个分布式集群的管理工具,保证集群的安全性是其一个重要的任务。API Server 是集群内部各个组件通信的中介,也是外部控制的入口。所以 Kubernetes 的安全机制基本就是围绕保护 API Server 来设计的。Kubernetes 使用了认证(Authentication)、鉴权(Authorization)、准入控制(Admission Control)三步来保证API Server的安全,称为 3A 服务。
一、认证
- HTTP Token 认证:通过一个 Token 来识别合法用户。
HTTP Token 的认证是用一个很长的特殊编码方式的并且难以被模仿的字符串 - Token 来表达客户的一种方式。Token 是一个很长的很复杂的字符串,每一个 Token 对应一个用户名存储在 API Server 能访问的文件中。当客户端发起 API 调用请求时,需要在 HTTP Header 里放入 Token** - HTTP Base 认证:通过用户名+密码 的方式认证。
用户名+:+密码 用 BASE64 算法进行编码后的字符串放在 HTTP Request 中的 Heather Authorization 域里发送给服务端,服务端收到后进行编码,获取用户名及密码** - 最严格的 HTTPS 证书认证:基于 CA 根证书签名的客户端身份认证方式**。
1.1、HTTPS 证书认证
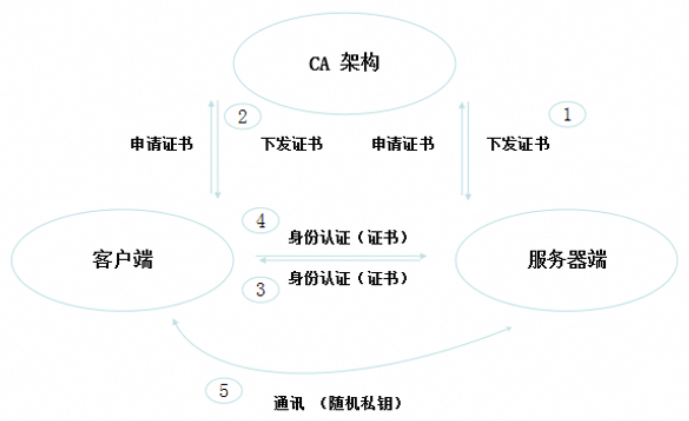
HTTPS 加密:
单向认证:客户端认证服务器端。
双向认证:客户端与服务器端互相认证。
1.2、需要认证的节点
两种类型:
(1)Kubenetes 组件对 API Server 的访问:kubectl、Controller Manager、Scheduler、kubelet、kube-proxy。
(2)Kubernetes 管理的 Pod 对容器的访问:Pod(dashborad 也是以 Pod 形式运行)。

安全性说明:
(1)Controller Manager、Scheduler 与 API Server 在同一台机器,所以直接使用 API Server 的非安全端口访问,--insecure-bind-address=127.0.0.1
(2)kubectl、kubelet、kube-proxy 访问 API Server 就都需要证书进行 HTTPS 双向认证。
证书颁发:
(1)手动签发:通过 k8s 集群的跟 ca 进行签发 HTTPS 证书**
(2)自动签发:kubelet 首次访问 API Server 时,使用 token 做认证,通过后,Controller Manager 会为 kubelet 生成一个证书,以后的访问都是用证书做认证了**
1.3、kubeconfig
kubeconfig 文件包含集群参数(CA证书、API Server地址),客户端参数(上面生成的证书和私钥),集群 context 信息(集群名称、用户名)。Kubenetes 组件通过启动时指定不同的 kubeconfig 文件可以切换到不同的集群。
1.4、ServiceAccount
Pod 中的容器访问API Server。因为Pod的创建、销毁是动态的,所以要为它手动生成证书就不可行了。Kubenetes使用了Service Account解决Pod 访问API Server的认证问题。
1.5、Secret 与 SA 的关系
Kubernetes 设计了一种资源对象叫做 Secret,分为两类,一种是用于 ServiceAccount 的 service-account-token, 另一种是用于保存用户自定义保密信息的Opaque。ServiceAccount 中用到包含三个部分:Token、ca.crt、namespace。
(1)token是使用 API Server 私钥签名的 JWT。用于访问API Server时,Server端认证。
(2)ca.crt,根证书。用于Client端验证API Server发送的证书。
(3)namespace, 标识这个service-account-token的作用域名空间。
1.5.1、创建SA实验
#创建张三的sa证书
kubectl create sa zhangsan --dry-run -o yaml
操作
#查看kube-system名称空间下的pod
kubectl get pod -n kube-system
#查看caloco-node绑定的SA
kubectl get pod calico-node-2pm9r -n kube-system -o yaml
#进入pod内的容器
kubectl exec -it calico-node-2pm9r -n kube-system -- /bin/sh
#切换到证书存放的目录
cd /run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/
ls
kubectl get secret --all-namespaces
#查看已存在的secret
kubectl describe secret -n kube-system default-token-5gm9r
默认情况下,每个 namespace 都会有一个 ServiceAccount,如果 Pod 在创建时没有指定 ServiceAccount,就会使用 Pod 所属的 namespace 的 ServiceAccount。
默认挂载目录:/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/。

二、鉴权
2.1、Authorization
上面认证过程,只是确认通信的双方都确认了对方是可信的,可以相互通信。而鉴权是确定请求方有哪些资源的权限。API Server 目前支持以下几种授权策略 (通过 API Server 的启动参数 “--authorization-mode” 设置)。
AlwaysDeny表示拒绝所有的请求,一般用于测试。AlwaysAllow允许接收所有请求,如果集群不需要授权流程,则可以采用该策略。ABAC(Attribute-Based Access Control)基于属性的访问控制,表示使用用户配置的授权规则对用户请求进行匹配和控制。Webhook通过调用外部 REST 服务对用户进行授权。RBAC(Role-Based Access Control)基于角色的访问控制,现行默认规则。
2.2、RBAC 授权模式
RBAC(Role-Based Access Control,基于角色的访问控制) 在 k8s v1.5 中引入,在 v1.6 版 本时升级为 Beta 版本,并成为 kubeadm 安装方式下的默认选项,相对于其他访问控制方式, 新的 RBAC 具有如下优势:
(1)对集群中的资源和非资源权限均有完整的覆盖。
(2)整个 RBAC 完全由几个 API 对象完成,同其他 API 对象一样,可以用 kubectl 或 API 进行操作。
(3)可以在运行时进行调整,无需重启 API Server。
要使用 RBAC 授权模式,需要在 API Server 的启动参数中加上--authorization-mode=RBAC。
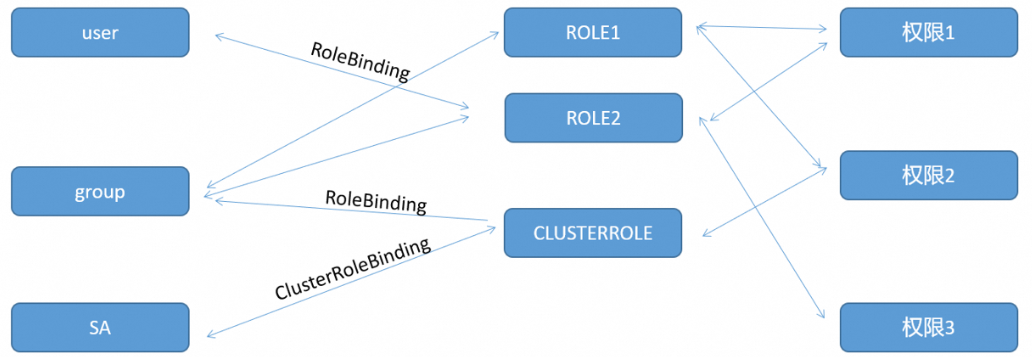
在集群里面又三个附着点:user(用户),group(组),SA(serviceaccount)(pod访问serviec的一个认证),一个角色可以背绑定给多个用户,一个用户可以绑定多个角色,权限和角色也是多对多的关系。
用户绑定角色的过程,这条线(关联)就是一个对象,这个对象叫RoleBinding(角色绑定),RoleBinding被创建时,这条线就被连上了,RoleBinding 被删除时,这条线就断了。
集群角色绑定就是ClusterBinding,也就是说,角色进行角色绑定,集群角色进行集群角色绑定。需要注意的是:集群角色被角色绑定而绑定。
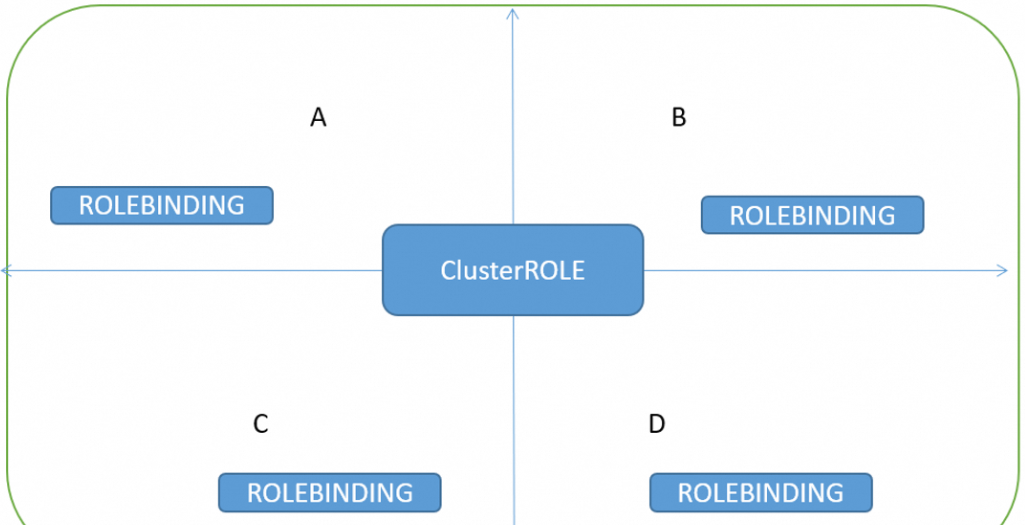
- ROLE ROLEBINDING #角色被角色绑定
- CLUSTERROLE CLUSTERROLEBINDING #集群角色被集群角色绑定
- CLUSTERROLE ROLEBINDING #集群角色被角色绑定
三、RBAC 原理和用法
3.1、RBAC 的 API 资源对象说明
RBAC 引入了 4 个新的顶级资源对象:Role、ClusterRole、RoleBinding、 ClusterRoleBinding。同其他 API 资源对象一样,用户可以使用 kubectl 或者 API 调用等方式操作这些资源对象。
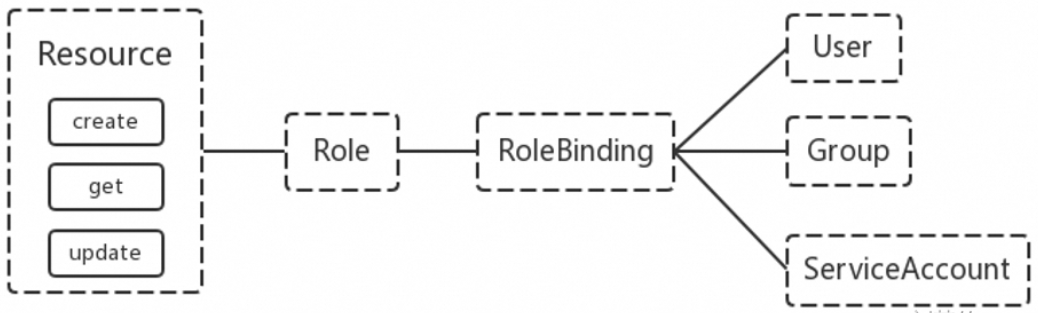
需要注意的是 Kubenetes 并不会提供用户管理,那么 User、Group、ServiceAccount 指定的用户又是从哪里来的呢? Kubenetes 组件(kubectl、kube-proxy)或是其他自定义的用户在向 CA 申请证书时,需要提供一个证书请求文件。
CFSSL #申请证书的工具
coreos 公司开发的基于 Golang 语言编写的证书签发工具,这个工具允许我们通过json文件作为我们证书生成的模板,生成证书签发证书,是一个简化的证书生成工具。
证书签发描述文件:
{
"CN": "admin", #将CN当作用户字段。冒号后面写什么,就代表是什么用户。
"hosts": [], #允许使用这个证书的地址,如果不写代表所用用户都可以使用这个证书
"key": {
"algo": "rsa", #加密算法使用rsa加密算法
"size": 2048 #2048位字符
},
"names": [
{
"C": "CN",
"ST": "HangZhou",
"L": "XS",
"O": "system:masters", #O字段,组字段,冒号后面跟什么就是什么组。
"OU": "System"
}
]
}
API Server会把客户端证书的CN字段作为。User,把names.O字段作为。Group。
kubelet 使用 TLS Bootstaping 认证时,API Server 可以使用 Bootstrap Tokens 或者 Token authentication file 验证=token,无论哪一种,Kubenetes 都会为 token 绑定一个默认的 User 和 Group。
Pod使用 ServiceAccount 认证时,service-account-token 中的 JWT 会保存 User 信息。
有了用户信息,再创建一对角色/角色绑定(集群角色/集群角色绑定)资源对象,就可以完成权限绑定了。
3.1.1、角色(Role)
一个角色就是一组权限的集合,这里的权限都是许可形式的,不存在拒绝的规则。在一个命名空间中,可以用角色来定义一个角色,如果是集群级别的,就需要使用 ClusterRole 了。角色只能对命名空间内的资源进行授权,下面的例子中定义的角色具备读取 Pod 的权限:
rule.yaml
kind: Role # 资源类别,用户组类型
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 # 组类别版本
metadata:
namespace: default # 角色是名称空间里面的,所以一定要写名称空间,如果不写,默认就在 defaults 名称空间下。
name: pod-reader # 当前角色名字为 pod-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group
# 规则指定当前操作对象的兼容的组版本,什么都没写,默认为核心组 v1 版。
resources: ["pods"] # 操作对象为 pod,兼容的组版本为核心组 v1 版
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
# 允许的动作类型,这里是:获取,监视,列出,这几个是当前 k8s 集群中抽象出来的动作类型。
rules 中的参数说明:
apiGroup支持的 API 组列表,例如:APIVersion: batch/v1、APIVersion: extensions:v1、apiVersion:apps/v1 等。resources支持的资源对象列表,例如:pods、deployments、jobs 等。verbs对资源对象的操作方法列表,例如:get、watch、list、delete、 replace 等。
3.1.2、集群角色(ClusterRole)
ClusterRole 具有与 Role 相同的权限角色控制能力,不同的是 ClusterRole 是集群级别的,ClusterRole 可以用于:
(1)集群级别的资源控制( 例如 node 访问权限 )
(2)非资源型 endpoints( 例如 /health 访问 )
(3)所有命名空间资源控制(例如 pods )
下面的集群角色可以让用户有权访问任意一个或所有命名空间的 secrets:
clusterrole.yaml
kind: ClusterRole # 集群角色类型
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 # 操作集群角色的组和版本
metadata: # 元数据
# "namespace" omitted since ClusterRoles are not namespaced
name: secret-reader # 当前集群角色的名称
rules: # 规则
- apiGroups: [""] # 操作当前集群角色的兼容组版本
resources: ["secrets"]
# 操作当前集群角色的对象为 secrets,他的组和版本为核心组 v1 版,所以上方可以不写。
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"] # 允许的操作类型
3.1.3、角色绑定(RoleBinding) & 集群角色绑定(ClusterRoleBinding)
角色绑定或集群角色绑定用来把一个角色绑定到一个目标上,绑定目标可以是 User、 Group 或者 Service Account。使用 RoleBinding 为某个命名空间授权, ClusterRoleBinding 为集群范围内授权。
RoleBinding 可以引用 Role 进行授权。下例将在 default 命名空间中把 pod-reader 角色授予用户 jane,可以让 jane 用户读取 default 命名空间的 Pod:
rolebinding.yaml
kind: RoleBinding # 角色绑定类型
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 # 监控主版本
metadata:
name: read-pods # 角色绑定的名称为 read-pods
namespace: default # 放在 default 名称空间下
subjects: # 绑定给哪个类型呢
- kind: User # 绑定给用户类型(类型可以写三种:用户,组,SA)
name: jane # 哪个用户呢,名为 jane 的用户
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef: # 角色来源于谁呢
kind: Role # 来源于角色类型
name: pod-reader # 哪个角色呢,名为 pod-reader 的角色,pod-reader 角色在上面已经创建了
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
# 达到的效果:jane 用户在 default 名称空间下,能够对 pod 有获取,列出,监听的权限。
# jane 用户怎么来的呢?证书里的 CN 字段得到的
RoleBinding 也可以引用 ClusterRole,对属于同一命名空间内 ClusterRole 定义的资源主 体进行授权。一种常见的做法是集群管理员为集群范围预先定义好一组角色(ClusterRole), 然后在多个命名空间中重复使用这些 ClusterRole。
使用 RoleBinding 绑定集群角色 secret-reader,使 dave 只能读取 development 命名空间中的 secret:
rolebinding-clusterrole.yaml
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: read-secrets
namespace: development
subjects:
- kind: User
name: dave
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: secret-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
#理论上有这个集群角色,可以在所有名称空间下去读取secret对象,但现在做的是角色绑定,dave用户,只能在dev名称空间下,行使这个权限(读取secret)。
集群角色绑定中的角色只能是集群角色,用于进行集群级别或者对所有命名空间都生效授权。允许 manager 组的用户读取任意 namespace 中的 secret。
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: read-secrets-global
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: manager
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: secret-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
3.2、对资源的引用方式
多数资源可以用其名称的字符串来表达,也就是 Endpoint 中的 URL 相对路径,例如 pods。 然后,某些 Kubernetes API 包含下级资源,例如 Pod 的日志(logs)。Pod 日志的 Endpoint 是 GET /api/v1/namespaces/{namespaces}/pods/{name}/log。
Pod 是一个命名空间内的资源,log 就是一个下级资源。要在一个 RBAC 角色中体现,则需 要用斜线/来分割资源和下级资源。若想授权让某个主体同时能够读取 Pod 和 Pod log,则 可以配置 resources 为一个数组:
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-and-pod-logs-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods", "pods/log"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
资源还可以通过名字(ResourceName)进行引用。在指定 ResourceName 后,使用 get、 delete、update、patch 动词的请求,就会被限制在这个资源实例范围内。例如下面的声 明让一个主体只能对一个叫 my-configmap 的 configmap 进行 get 和 update 操作:
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: configmap-updater
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmap"]
resourceNames: ["my-configmap"]
verbs: ["update", "get"]
3.3、常见的角色(Role)示例
(1)允许读取核心 API 组中 Pod 的资源:
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
(2)允许读写"extensions"和"apps"两个 API 组中的 deployment 资源
rules:
- apiGroups: ["extensions", "apps"]
resources: ["deployments"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]
(3)允许读写 pods 及读写 jobs
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["batch", "extensions"]
resources: ["jobs"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]
(4)允许读取一个名为 my-config 的 ConfigMap(必须绑定到一个 RoleBinding 来限制到 一个 namespace 下的 ConfigMap):
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
resourceNames: ["my-config"]
verbs: ["get"]
(5)读取核心组的 node 资源(Node 属于集群级别的资源,必须放在 ClusterRole 中,并 使用 ClusterRoleBinding 进行绑定):
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
(6)允许对非资源端点/healthz 及其所有子路径进行 GET/POST 操作(必须使用 ClusterRole 和 ClusterRoleBinding):
rules:
- nonResourceURLs: ["/healthz", "/healthz/*"]
verbs: ["get", "post"]
3.4、常用的角色绑定
- 用户名 Alice@example.com
subjects:
- kind: User
name: "Alice@example.com"
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- 组名 frontend-admins
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: "frontend-admins"
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- kube-system 命名空间中的默认 Service Account
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: default
namespace: kube-system
- qa 命名空间中的所有 Service Account
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:serviceaccounts:qa
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- 所有 Service Account
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:serviceaccounts
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- 所有认证用户
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:authentication
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- 所有未认证用户
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:unauthentication
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- 全部用户
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:authentication
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- kind: Group
name: system:unauthentication
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
3.5、默认的角色和角色绑定
API Server 会创建一套默认的 ClusterRole 和 ClusterRoleBinding 对象,其中很多是以 system:为前缀的,以表明这些资源属于基础架构,对这些对象的改动可能造成集群故障。
所有默认的 ClusterRole 和RoleBinding 都会用标签 kubernetes.io/bootstrapping=rbac-defaults 进行标记。
常见的系统角色如下:

有些默认角色不是以 system:为前缀的,这部分角色是针对用户的,其中包含超级用户角色 cluster-admin,有的用于集群一级的角色 cluster-status,还有针对 namespace 的角色 admin、edit、view。
常见的用户角色如下:

核心 Master 组件角色
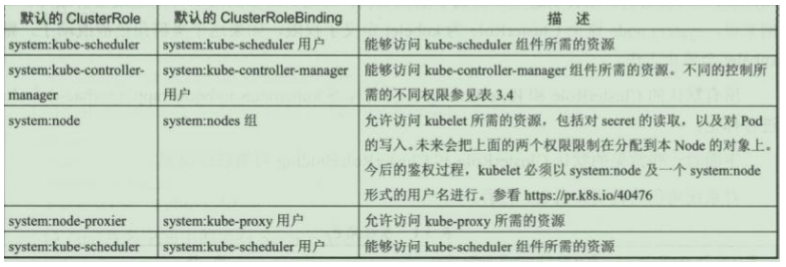
3.6、授权注意事项:预防提权和授权初始化
RBAC API 拒绝用户利用编辑角色或者角色绑定的方式进行提权。这一限制是在 API 层 面做出的,因此即使 RBAC 没有启用也仍然有效。
用户只能在拥有一个角色的所有权限,且与该角色的生效范围一致的前提下,才能对 角色进行创建和更新。例如用户 user-1 没有列出集群中所有 secret 的权限,就不能创建 具有这一权限的集群角色。要让一个用户能够创建或更新角色,需要以下权限:
为其授予一个允许创建/更新 Role 或 ClusterRole 资源对象的角色;
为用户授予角色,要覆盖该用户所能控制的所有权限范围。用户如果尝试创建超出 其自身权限的角色或者集群角色,则该 API 调用会被禁止。
如果一个用户的权限包含了一个角色的所有权限,那么就可以为其创建和更新角色绑 定;或者如果被授予了针对某个角色的绑定授权,则也有权完成此操作。
例如:user1 没有列出集群内所有 secret 的权限,就无法为一个具有这样权限的角色 创建集群角色绑定。要使用户能够创建、更新这一角色绑定,则需要有如下做法:
为其授予一个允许创建和更新角色绑定或者集群角色绑定的角色。
为其授予绑定某一角色的权限,有隐式或显式两种方法。
隐式:让其具有所有该角色的权限。
显式:让用户授予针对该角色或集群角色绑定操作的权限。
让 user-1 有对 user-1-namespace 命名空间中的其他用户授予 admin、edit 及 view 角色。
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: role-grantor
rules:
- apiGroups: ["rbac.authorization.k8s.io"]
resources: ["rolebindings"]
verbs: ["create"]
- apiGroups: ["rbac.authorization.k8s.io"]
resources: ["clusterroles"]
verbs: ["bind"]
resourceNames: ["admin", "edit", "view"]
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: role-grantor-binding
namespace: user-1-namespace
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: role-grantor
subjects:
- apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: User
name: user-1
在进行第一个角色和角色绑定时,必须让初始用户具备其尚未被授予的权限,要进行初始 的角色和角色绑定设置,有以下两种方法:
使用属于 system:masters 组的身份,这一群组默认具有 cluster-admin 这一超级角色的绑定。
如果 API Server 以 --insecure-port 参数运行,则客户端通过这个非安全端口进行 接口调用,这一端口没有认证鉴权的限制。
四、准入控制
准入控制是API Server的插件集合,通过添加不同的插件,实现额外的准入控制规则。甚至于API Server的一些主要的功能都需要通过 Admission Controllers 实现,比如 ServiceAccount。
插件列表:
NamespaceLifecycle,LimitRanger,ServiceAccount,DefaultStorageClass,
DefaultTolerationSeconds,MutatingAdmissionWebhook,ValidatingAdmissionWebhook,
ResourceQuota
列举几个插件的功能:
NamespaceLifecycle防止在不存在的 namespace 上创建对象,防止删除系统预置 namespace,删除 namespace 时,连带删除它的所有资源对象。LimitRanger确保请求的资源不会超过资源所在 Namespace 的 LimitRange 的限制。ServiceAccount实现了自动化添加 ServiceAccount。ResourceQuota确保请求的资源不会超过资源的 ResourceQuota 限制。
以devuser用户登录终端
#这个default本质上就是我们的ServiceAccount,我们并没有创建,他是自己自动创建出来的
#这就是ServiceAccount插件的含义,每创建一个名称空间,他就会自动在当前的名称空间下创建一个default ServiceAccount
kubectl get sa -n dev

评论